Spring is around the corner, and tree buds are breaking. Now is the time to be aware of three common leaf diseases that can invade your trees: anthracnose, aspen leaf spot, and coryneum blight.


Read this post to learn what these diseases look like and how to treat them.
Anthracnose Tree Fungus
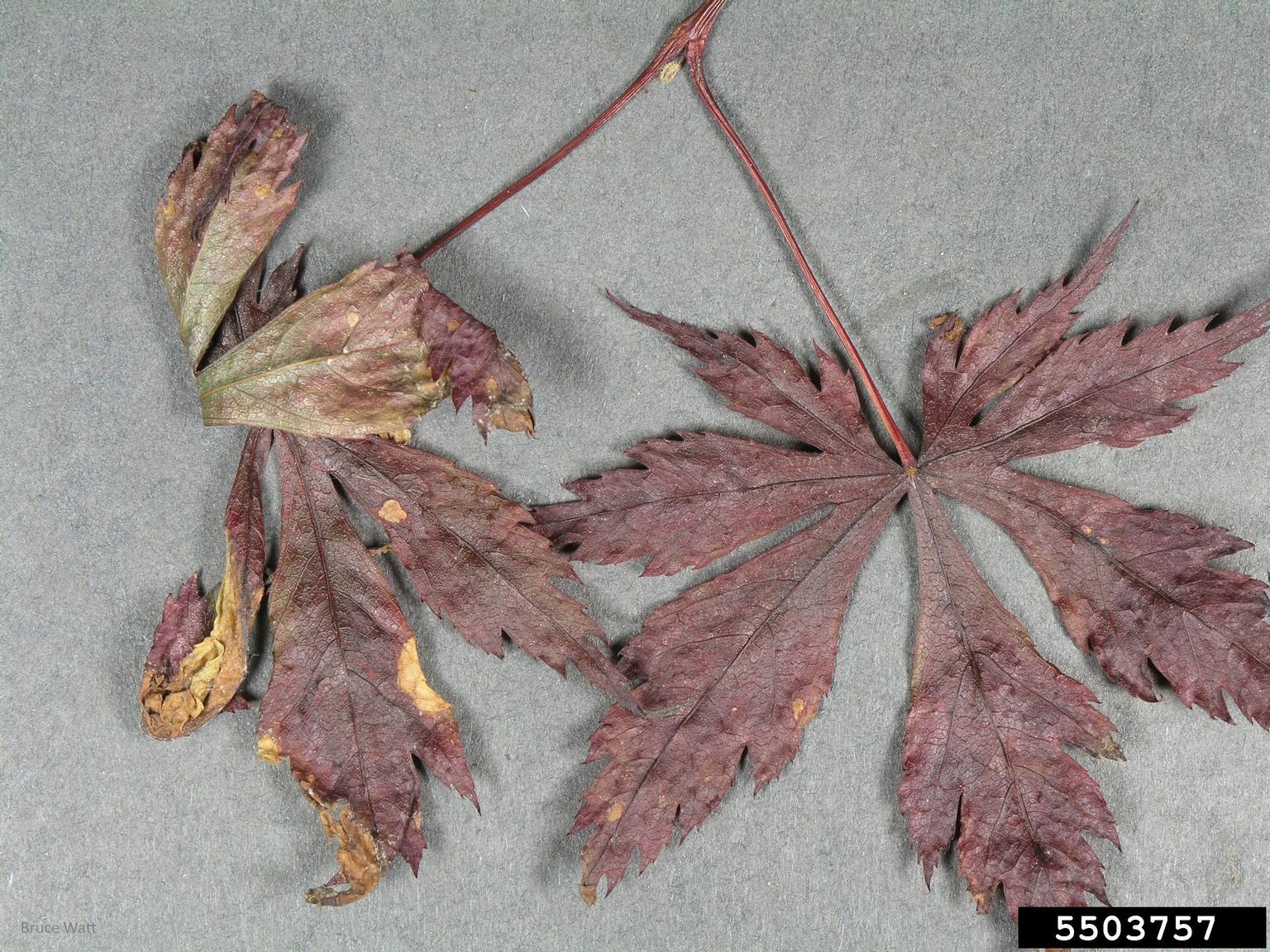
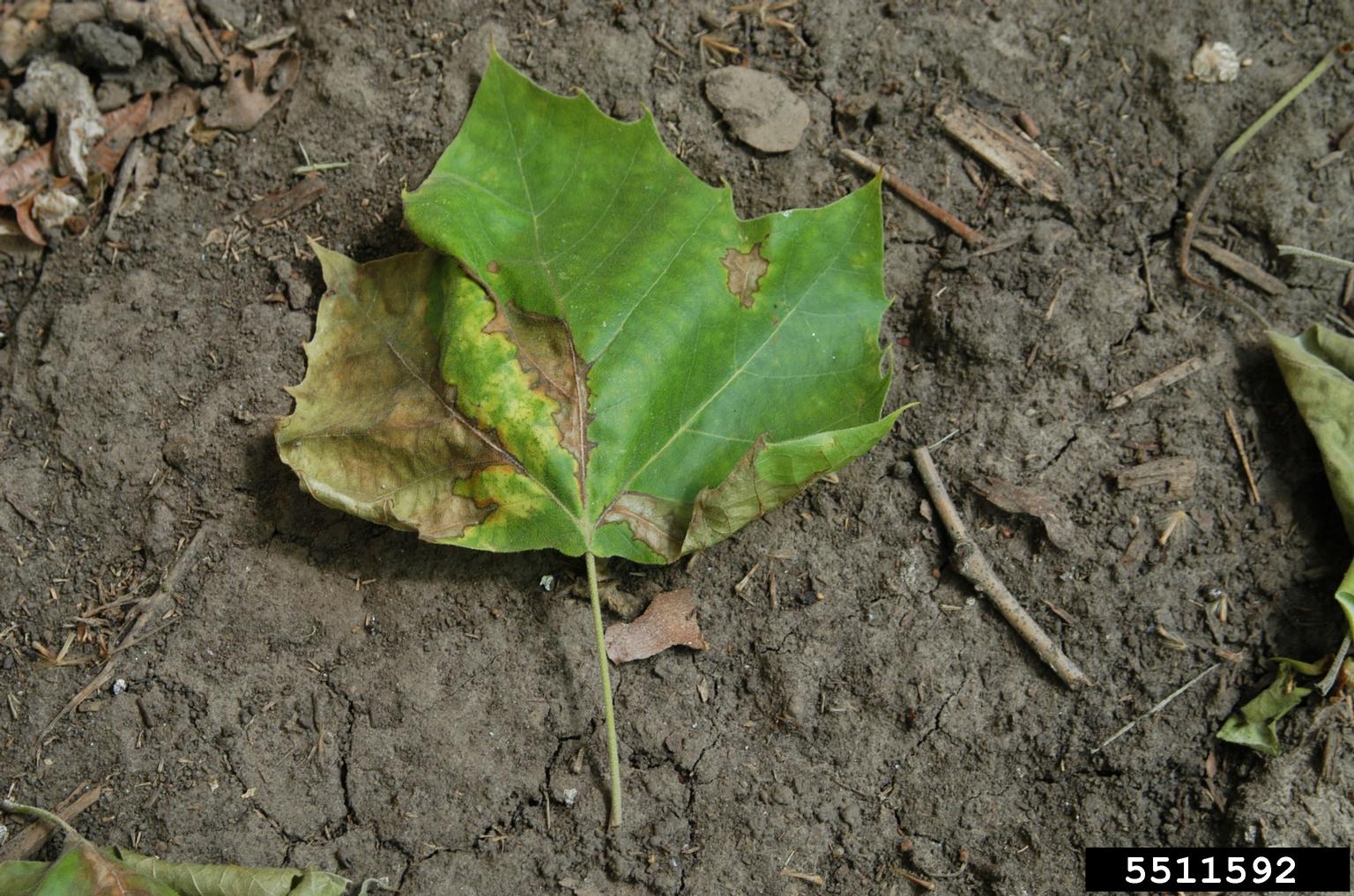
Anthracnose is a fungal disease that occurs in Utah on ash, dogwood, maple, oak, and sycamore trees. The fungus causes brown and tan lesions on leaves—usually along the main veins. As the disease worsens, the lesions grow to take up large portions of the leaves.


Tree branches can also become infected with the anthracnose fungus. The fungus creates black spots on the bark of the branches. As anthracnose gets worse, the bark starts to split.
To help prevent anthracnose from developing on your trees, try doing the following:
- Plant trees that are resistant to the fungus
- Leave plenty of space between trees
- Prune your trees properly
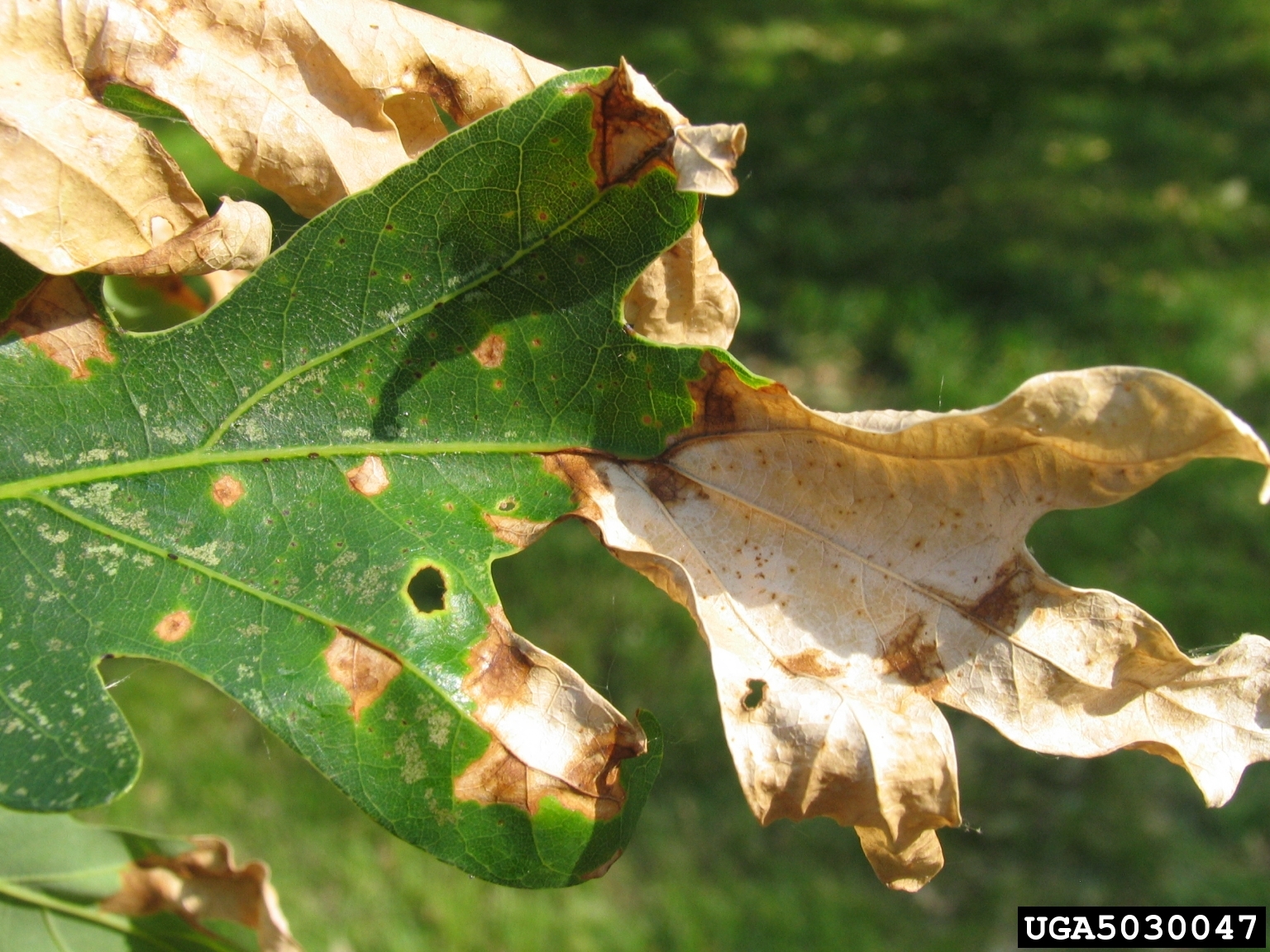


Anthracnose on Oak Tree; Joseph OBrien, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Anthracnose usually affects the twigs and leaves of the tree. It survives the winter months in dead leaves on the ground and in infected twigs. In the spring, it spreads through splashing rain and wind. One way to help prevent the spread of this fungus is to rake up dead leaves in the fall.
At its mild stages (when it’s only in the leaves), this disease can be treated with a leaf disease control spray. Once it enters the twigs and branches of the tree, injections are needed in order to treat anthracnose. However, injections are expensive and sometimes ineffective. Stewarts offers leaf disease control sprays and tree injections as part of its tree treatment programs.
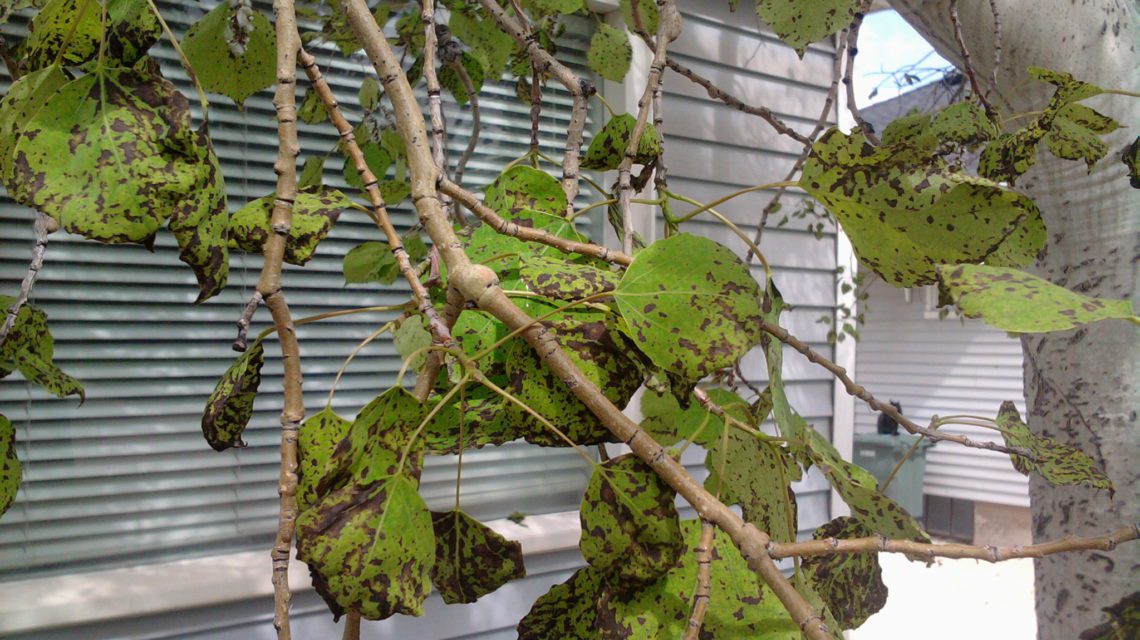
Aspen Leaf Spot Disease
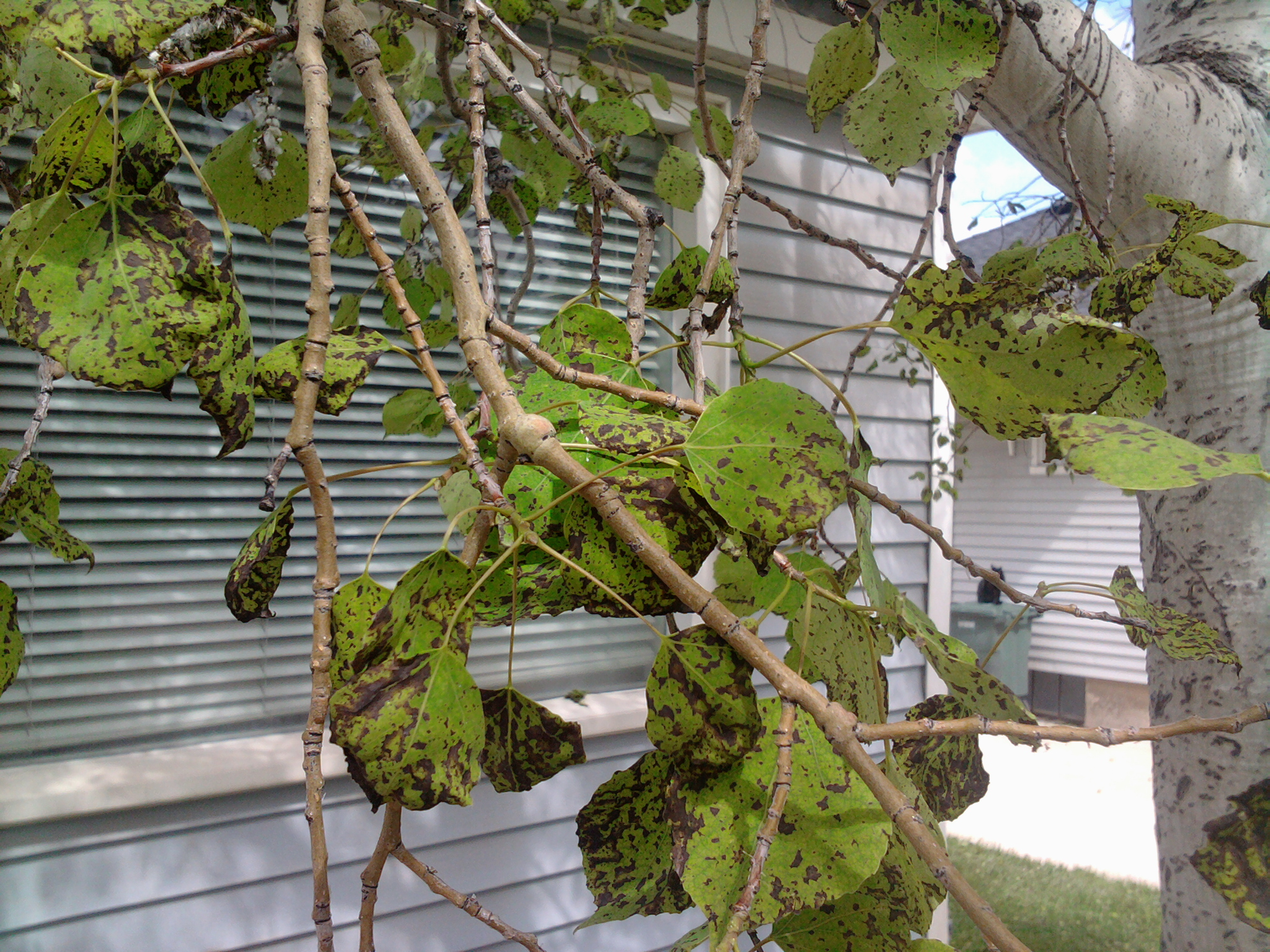


Aspen leaf spot is quite common in aspens and other poplar tree varieties. The disease creates brown spots with yellow rings on leaves. If left untreated, the lesions will grow and eventually deteriorate, leaving holes. Because the tree is under stress due to the disease, it can also become susceptible to problems like aspen borer, iron chlorosis, or other related issues.
Some actions can be taken to help prevent aspen leaf spot:
- Prevent sprinklers from getting leaves wet (especially lower leaves)
- Properly dispose of leaves in the fall
- Prune branches properly
- Leave plenty of space between trees so air can circulate well around them
The fungus that causes aspen leaf spot is spread through wind and rain in the springtime. It lives in dead leaves during the winter and creates spores (that allow it to spread) in the spring. This disease is generally not lethal to the tree by itself. However, when combined with other problems, aspen leaf spot disease can contribute to the death of the tree.
Coryneum Blight Tree Fungus
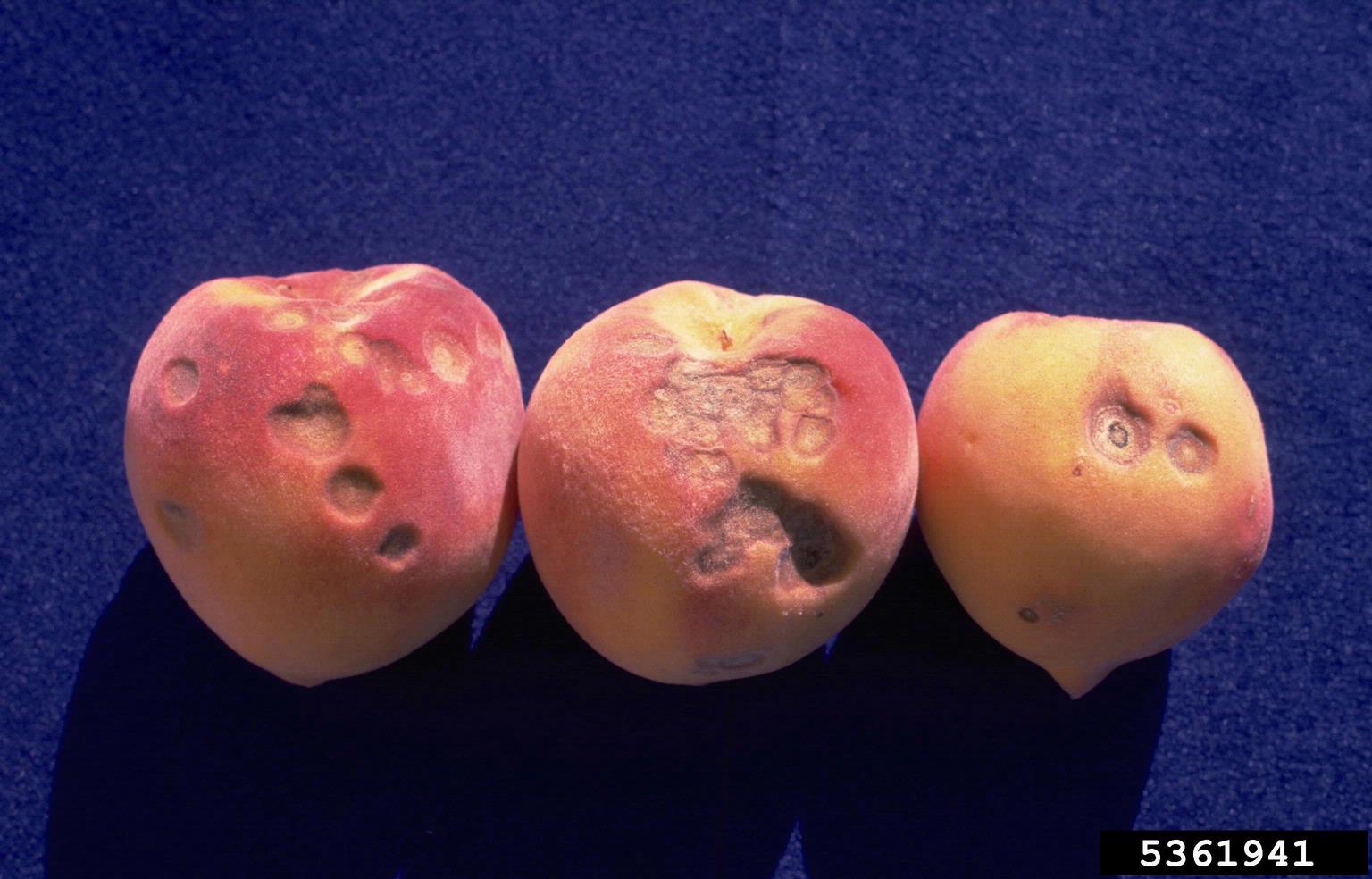

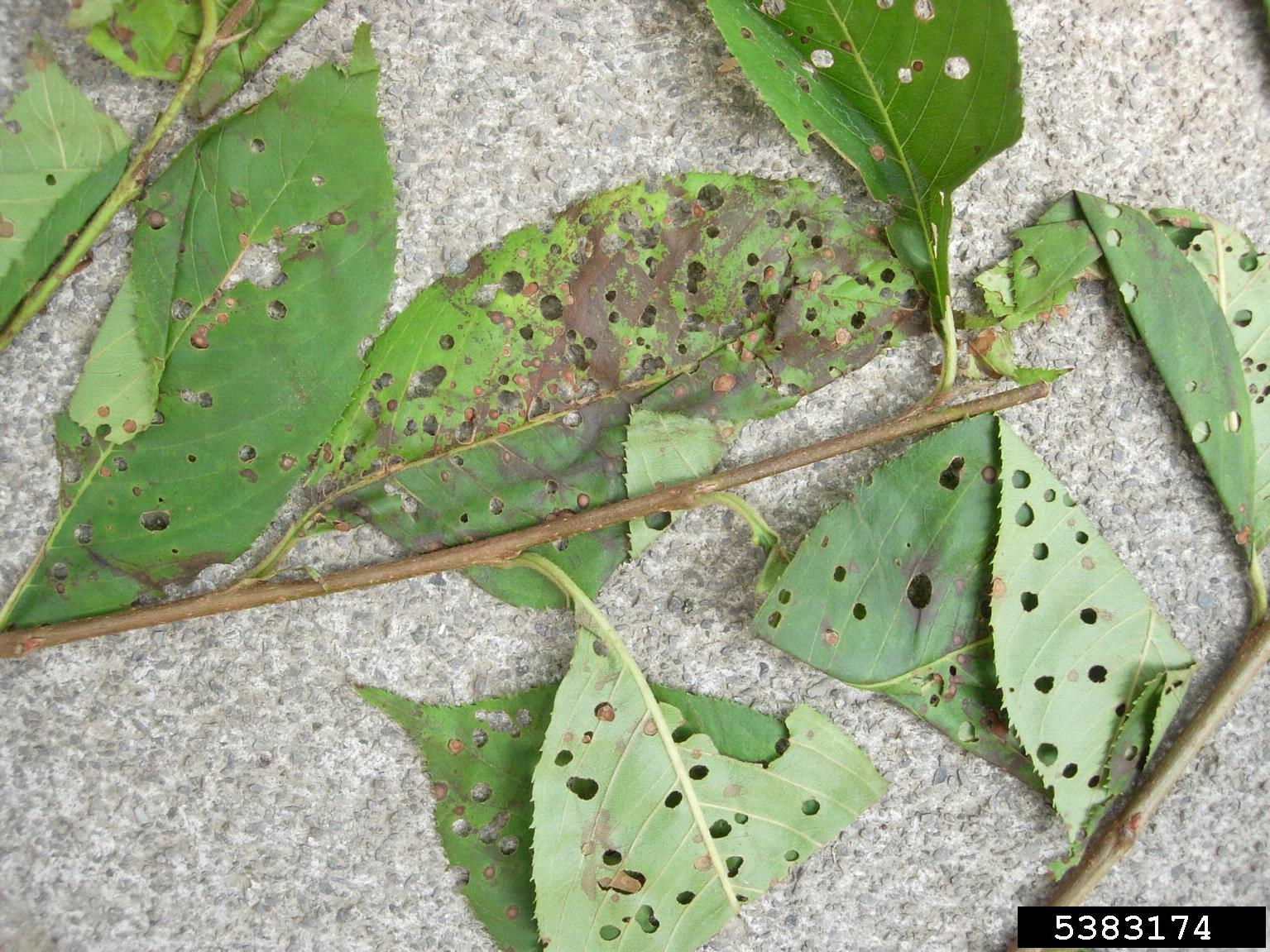
Coryneum blight is a fungal disease found in ornamental (flowering) and stone fruit trees, especially apricot, nectarine, and peach trees. The infection can affect branches, buds, fruit, and leaves. The disease first appears as purple or brown small, circular spots on leaves. As the summer progresses, the spots fall out, leaving small round holes within the leaf margins. The round holes have led to the disease being called another name: shothole blight.


The fungus also causes brown and purple spots on the fruit that eventually turn into white and gray lesions. The lesions then crack and seep fluid. If left untreated, the disease can cause loss of fruit over time.
Purple-red spots can also appear on twigs and branches. Infected buds will die, creating a dark, sunken circle on the branch or twig around the bud.
Containing it is difficult, but coryneum blight is preventable:
- Remove and dispose of infected leaves and branches in the fall
- Apply fungicides in the fall to prevent infections that will appear on the leaves in the spring
Similar to other fungal diseases, coryneum blight is spread through splashing rain in the spring. This disease spends the winter in tree buds and twigs and then spreads during the spring and summer.
Treatments
One way to treat these diseases is to prune the infected sections of the tree. Sanitize the pruning tool with alcohol or bleach in between each cut to ensure the disease doesn’t spread.
Stewart’s offers a fungus control for trees. We spray trees in the spring after the buds have broken and before the leaves are fully grown. The treatment helps infected trees and prevents leaf diseases from spreading.
For a free service estimate, call or text us at 801-226-2261.
Sources:
https://utahpests.usu.edu/ipm/notes_orn/list-treeshrubs/anthracnose
https://utahpests.usu.edu/ipm/notes_orn/list-treeshrubs/aspen-leaf-spot
http://www.intermountainfruit.org/dbm/shothole
http://ipm.ucanr.edu/PMG/PESTNOTES/pn7420.html
https://www.extension.uidaho.edu/publishing/pdf/CIS/CIS1202.pdf
Watch our three videos about common sycamore tree leaf problems
Sycamore anthracnose:
Sycamore plant bug:
Sycamore scale:



